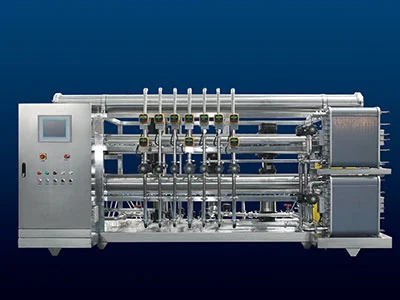
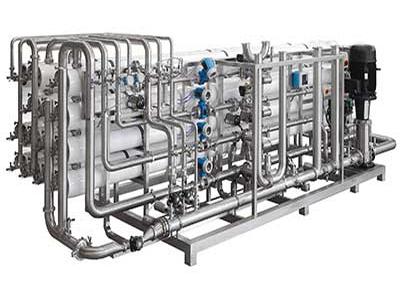
In the field of biopharmaceuticals,the design of water-for-injection systems is critically important. These systems need to ensure that the water provided reaches extremely high purity levels to meet the strict requirements of production and experiments. This article will delve into the design essentials of water-for-injection systems, covering preparation systems, storage, pump design, distribution piping, sterilization, and user point design.
Preparation Methods of Water-for-Injection Systems
Water-for-injection systems' core lies in its preparation process. The distillation method is the most commonly used method, as it can steadily produce high-quality water while simultaneously sterilizing. This method is widely adopted globally and is the preferred choice for water for injection systems. In contrast, while the reverse osmosis method is also recognized by the United States Pharmacopeia, its stability is relatively poor because it operates at room temperature and does not have effective antimicrobial contamination resistance. In China, water-for-injection systems usually use the distillation method, as it meets the requirements of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and ensures the purity of the water.
Storage Design of Water-for-Injection Systems
Storage design is a critical link in water-for-injection systems. The storage tank should be made of high-quality stainless steel materials (such as 316L) and equipped with an electric signal level control device to ensure safety and sanitation. To prevent microbial contamination from the air, a hydrophobic vent filter with a pore size of 0.22μm needs to be installed on the top of the tank, generally made of PTFE or PVDF materials. Additionally, to maintain water temperature, the tank needs to be designed to continuously maintain the temperature, which should be controlled above 80℃ or below 4℃. The capacity design should consider continuous circulation operation and water level height to meet actual usage needs and return water volume.
Pump Design of Water-for-Injection Systems
In water-for-injection systems, the design of the water pump needs to consider hygiene and ease of cleaning. The pump casing and open impeller should be made of 316L stainless steel to ensure durability and cleanliness. The pump angle is generally controlled around 45° to reduce the chance of air entering the pump body, ensuring the normal operation of the water pump. To improve energy efficiency, it is recommended to use a variable-frequency pump and avoid using standby pumps to reduce energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Distribution Piping Design of Water-for-Injection Systems
The distribution piping design is crucial for the stability of water-for-injection systems. The piping needs to maintain a stable turbulence state, with a flow rate controlled between 1~3m/s. The slope should ensure that the water can be completely drained. When selecting fittings, the diameter of valves and pipes should be considered to meet actual needs. Typically, it is recommended to use eccentric sanitary diaphragm valves to enhance system rationality and efficiency.
Sterilization Design of Water-for-Injection Systems
Sterilization is a critical step in ensuring the water quality of water-for-injection systems. Pure steam pressure sterilization is a commonly used method, with the pressure controlled between 0.1~0.3MPa and the sterilization time generally no less than 1 hour. Additionally, superheated water-for-injection sterilization is also frequently used in such systems. The temperature needs to reach 121℃, with sterilization and disinfection carried out through the circulation system, and the sterilization time should also not be less than 1 hour.
User Point Design of Water-for-Injection Systems
Every user point design should be based on actual needs, such as water volume, water temperature, and water pressure. These demands not only affect the choice of system components but also relate to the economic efficiency and operational cost of the overall process. Therefore, discussing and confirming the distribution with the user department is an essential step in optimizing the design of water-for-injection systems.
In summary, the design of water-for-injection systems needs to consider multiple aspects, including preparation methods, storage, pump design, piping, sterilization, and user points. By reasonably designing and optimizing these components, the water-for-injection systems can ensure high-quality water sources that meet the strict requirements of the biopharmaceutical industry.